Artificial intelligence and robotics will affect almost all occupations, but how that will occur for each is unclear. Many people will be displaced by technology, while the demand for other jobs will increase. New industries will be born, and other as-yet-unimagined jobs created.
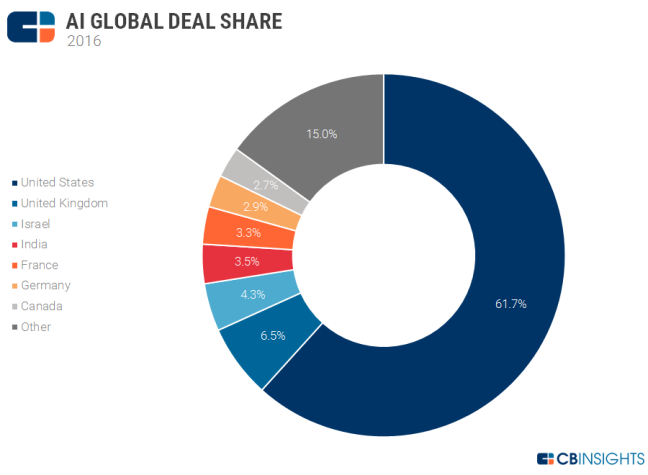
The Milan Theory describes a marketplace for IS fashion, where the Demand set by users of IS trends, based on Socio-psychological and techno-economic forces they experience. This demand is then acted upon by the Supply, who consists of Consultants, Gurus, Business Schools and Mass media. So who is promoting this trend and driving this fashion? Regarding the global market, the United States and the United Kingdom have a significant share of 70% of the market together with many European countries. Tech Giants like Google, Apple and Microsoft have invested over 1 billion dollars in driving AI innovation. We can already see the mass demand for the products and services generated by these organisations. Comparisons of the academic and practitioner world, the influencers are the practitioners with the academic community lagging behind.
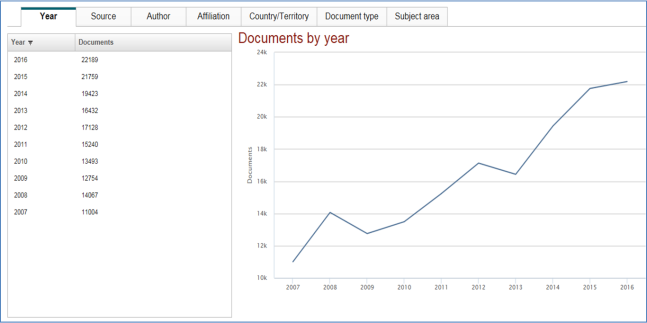
In the Herd Behaviour theory, when choosing to adopt ICT people go with the crowd’s choice when they are uncertain about their chose, sometimes even when it is not necessarily better than their choosing (Sun, 2013). Onalytica analysed 1.1M+ tweets from 30 November 2015 – 24 February 2016 mentioning the keywords “#AI OR “Artificial Intelligence” OR ArtificialIntelligence OR “Machine Learning” OR Machine learning” and identified the top 100 most influential brands and individuals leading the discussion on Twitter. The increase in both academic and practitioner publications in this move suggest that this is indeed a fashion.
It is apparent that Artificial Intelligence is indeed a fashion in IS that has been trending upwards and continued to do so.
References
Baskerville, R. L., & Myers, M. D. (2009). Fashion waves in information systems research and practice.Mis Quarterly, 647-662.
Sun, H. (2013). A longitudinal study of herd behavior in the adoption and continued use of technology.Mis Quarterly, 37(4), 1013-1041.